IssueOps Series: The GitHub Actions Toolkit for Jira Project Operations
Part-1: Automating Jira Issue operations with GitHub Actions
Overview
In the fast-paced world of software development, efficiency and automation are paramount. While Jira remains a cornerstone for project management, and GitHub is the de facto standard for code hosting and collaboration, bridging the gap between these two powerful platforms can significantly enhance your team's productivity. This blog post examines how GitHub Actions can serve as a valuable toolkit for automating and streamlining Jira project operations.
Jira, with its robust issue tracking and project management capabilities, enables teams to plan, track, and release software effectively. GitHub, on the other hand, is where the code lives, where development happens, and where continuous integration and delivery pipelines are built. Traditionally, synchronizing information and triggering actions between these systems often involved manual updates or complex, custom scripts. This is where GitHub Actions steps in, offering a flexible and powerful way to automate these interactions, bringing your project management and development workflows closer than ever.
Why Use GitHub Actions to Automate Jira Operations?
The benefits of integrating GitHub Actions with Jira are numerous:
Increased Efficiency: Eliminate manual data entry and repetitive tasks, allowing your team to focus on development.
Improved Accuracy: Reduce human error by automating updates and status changes.
Enhanced Visibility: Keep Jira updated in real-time with development progress, providing stakeholders with accurate project status.
Faster Feedback Loops: Automate notifications and issue creation based on code events, ensuring timely responses to critical issues.
Customization and Flexibility: GitHub Actions provides a vast marketplace of existing actions and the ability to create custom workflows tailored to your team's specific needs. Would recommend reading the Create Custom GitHub Actions blog post if you are interested in creating custom GitHub Actions.
Centralized Automation: Manage your project-related automation directly within your code repository, alongside your CI/CD pipelines.
In this blog post, I will try to showcase use cases for Jira, which could be automated with GitHub actions. This would be a two-part blog post. For this blog post/article, I would try to showcase some of the obvious use cases that could be automated for Jira using GitHub Actions, to improve development efficiency, allowing development teams to focus on actual product development. The other blog post would describe some of the use cases a project manager/scrum lead performs for better project management, providing stakeholders with accurate project status.
How to Get Started
To get started with building a GitHub Actions toolkit for Jira automation, one can do the following:
Search GitHub Marketplace: Search for existing actions for Jira Integration on the GitHub Marketplace.
Build Custom Actions: As you become more familiar, expand your toolkit with additional custom actions for tasks like adding comments, linking pull requests, etc.
Create First Workflow: Write a
.ymlfile in the.github/workflows/directory of your repository. This file will define the trigger for your automation (e.g., a new pull request or a code push) and the steps to execute.
Automation Use Cases
For this blog post, we would consider using a Custom GitHub Action (JavaScript Action) for integration with Jira that has already been created and published. Refer to this blog post Create Custom GitHub Actions, for more details on creating Custom GitHub Actions. There would be different workflows to support different use cases, which are triggered on different events on GitHub.
Create Jira Bug - On Pull Request from GitHub Dependabot
For this use case, a Jira Bug would be added to the Jira Board, on a Pull request from GitHub Dependabot. Whenever it scans and raises an alert for a vulnerable project dependency.
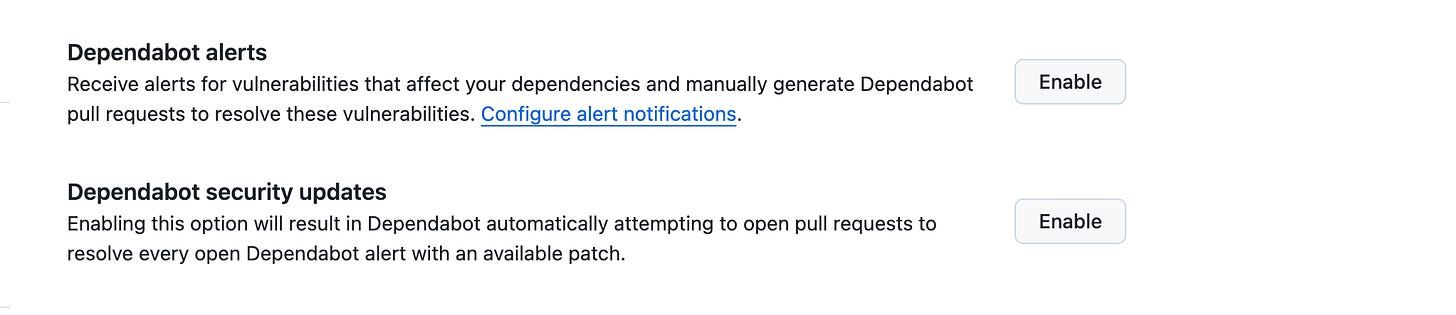
Enable Auto Pull Request feature - GitHub Dependabot
Go to Repository Settings → Security → Advanced Security → Dependabot → Enable Dependabot security updates
Create Workflow
Let’s create a workflow that creates a Jira bug when GitHub Dependabot raises a pull request to fix a vulnerable dependency. This Jira bug is to track and review the vulnerable dependency in the bug and the fix version of the dependency.
Workflow
name: Create Jira Issues Workflow
on:
pull_request:
branches: [ "master" ]
jobs:
create_jira_issue:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
node-version: [ 20.x ]
steps:
- name: Create Jira Issue
if: github.actor == 'dependabot[bot]'
uses: actions/issues-ops-jira@v1
with:
JIRA_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.JIRA_TOKEN }}
JIRA_API_HOST: ${{ secrets.JIRA_BASE_URL }}
JIRA_PROJECT: ${{ secrets.JIRA_PROJECT }}
JIRA_USER_EMAIL: ${{ secrets.JIRA_USER_EMAIL }}
JIRA_ISSUE_OPERATION: 'CREATE_ISSUE'
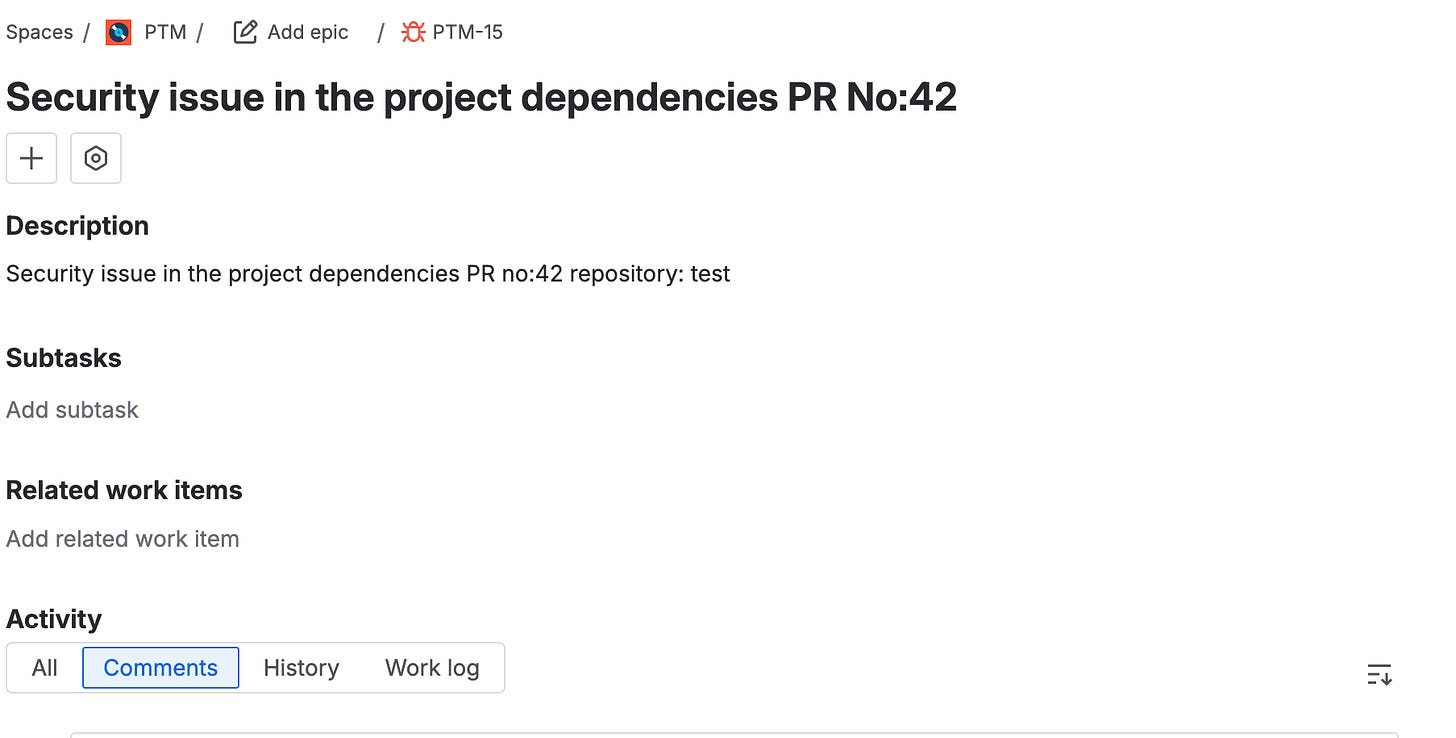
JIRA_JSON_INPUT: <<JSON-String-Create-Issue>>See the screenshot below of the Jira Bug added by the workflow on the Jira Board.
Jira Bug
Add PR link in Issue Comment
For this use case, there would be a separate workflow, which would be executed when a PR is raised on a specific branch. Below is a sample workflow file and the execution results for a Jira ticket or board.
Workflow
name: add-comment-update-issue-fields-jira.yml
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- master
jobs:
add-pr-link-comment-jira:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
node-version: [20.x]
steps:
- name: add comment and update fields jira
uses: actions/issues-ops-jira@v1
with:
JIRA_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.JIRA_TOKEN }}
JIRA_API_HOST: ${{ secrets.JIRA_BASE_URL }}
JIRA_PROJECT: ${{ secrets.JIRA_PROJECT }}
JIRA_USER_EMAIL: ${{ secrets.JIRA_USER_EMAIL }}
JIRA_ISSUE_OPERATION: 'UPDATE_ISSUE',
JIRA_JSON_INPUT: <<JSON-String>>Sample JavaScript code to add a comment and reviewers
async function updateIssue (issue,jiraClient) {
// add PR link to the issue
jiraClient.issueComments.addComment({
issueIdOrKey: issue.id,
comment: "PR link : " + issue.pr.link
}).then(res => {
console.log("PR link added to the issue, id: " + issue.id)
}).catch(error => {
console.log("Error adding PR link to the issue, id: " + issue.id)
core.setFailed(JSON.stringify({
message: "Error adding PR link to the issue",
id: issue.id,
error: error.message
}))
})
core.info(JSON.stringify({
message: "Issues updated successfully",
issueId: issue.id
}))
}
Updated Jira Ticket
Update Jira Ticket Status - On PR merge to the branch specific to the Environment
Here, the Workflow would update the Jira Ticket status when it’s merged to a certain target branch. Let’s say the Jira Ticket status is “In Progress”. The PR is raised for the Test Branch, which would be deployed on the Test environment. The workflow, upon successful execution on PR merge, will update the Jira Ticket status to “In Test”.
Workflow
name: update-status-jira-issue.yml
on:
push:
branches:
- test
jobs:
add-pr-link-comment-jira:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
node-version: [20.x]
steps:
- name: add comment and update fields jira
uses: actions/issues-ops-jira@v1
with:
JIRA_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.JIRA_TOKEN }}
JIRA_API_HOST: ${{ secrets.JIRA_BASE_URL }}
JIRA_PROJECT: ${{ secrets.JIRA_PROJECT }}
JIRA_USER_EMAIL: ${{ secrets.JIRA_USER_EMAIL }}
JIRA_ISSUE_OPERATION: 'UPDATE_ISSUE'
JIRA_JSON_INPUT: <<JSON-String>>Sample JavaScript code to update Jira Ticket status
async function updateIssue (issue,jiraClient) {
jiraClient.issues.editIssue({
id: issue.id,
transition: {
to: {
statusCategory: {
name: issue.status
}
}
},
fields: {
description: issue.description
}
}).then(res => {
console.log("Issue status updated for the issue, id: " + issue.id)
}).catch(error => {
console.log("Error updating issue status for the issue, id: " + issue.id)
core.setFailed(JSON.stringify( {
message: "Error updating issue status",
id: issue.id,
error: error.message
}))
})
core.info(JSON.stringify( {
message: "Issues updated successfully",
issueId: issue.id
}))
}Updated Jira Ticket
Conclusion
Ultimately, the synergy between Jira and GitHub Actions is about more than just automation—it's about creating a more efficient and harmonious development environment. The benefits are clear: faster feedback loops, reduced human error, and a single source of truth for project status. By automating the mundane tasks of issue management, teams can free up valuable time and focus on what truly matters: writing great code and delivering value to their users. This integration represents a significant step forward in streamlining the software development process and is a crucial tool for any team seeking to enhance their workflow.