GraphQL API with Spring Boot and MongoDB
Building Query APIs with GraphQL, SpringBoot and MongoDB.
Overview
In the rapidly evolving landscape of API development, GraphQL has emerged as a powerful alternative to traditional REST architectures, offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency in data fetching. When combined with the robust capabilities of Spring Boot for rapid application development and MongoDB for flexible, scalable data storage, developers can create highly performant and adaptable APIs.
This article explores the synergy of GraphQL, Spring Boot, and MongoDB, highlighting their strengths and how they collectively empower the creation of modern, data-driven applications.
Create a GraphQL-Springboot Application
Let’s create an application for the Store-Franchise use case to demonstrate the capabilities of using GraphQL with Spring Boot to create a query API, utilizing MongoDB as a data store.
Create Schema Definition
Let’s add the schema
schema.graphqls
scalar JSON
type Franchise {
id: String
name: String
description: String
isActive: Boolean
isDeleted: Boolean
created_at: String
updated_at: String
attributes: JSON
}
type Store {
id: String
name: String
franchiseId: String
description: String
created_at: String
updated_at: String
attributes: JSON
}
type Query {
storesByFranchise(id: String): [Store]
storesByFranchiseAndPincode(id: String, pincode: String): [Store]
storesByPincode(pincode: String): [Store]
franchiseById(id: String): Franchise
}Note: For the schema file, follow the directory structure mentioned below in the project directory
project-root-dir/
├── src/
│ └── main/
│ └── resources/
│ └── graphql/
│ └── schema.graphqlsCreate API Layer
Add an API layer to support querying the data store.
Store API
@Controller
public class StoreManagementQueryController {
private StoreManagementQueryService storeManagementQueryService;
public StoreManagementQueryController(StoreManagementQueryService storeManagementQueryService) {
this.storeManagementQueryService = storeManagementQueryService;
}
@QueryMapping
public List<Store> storesByFranchise(@Argument String id) {
return this.storeManagementQueryService.getStoresByFranchise(id);
}
@QueryMapping
public List<Store> storesByPincode(@Argument String pincode) {
return this.storeManagementQueryService.getStoresByPincode(pincode);
}
@QueryMapping
public List<Store> storesByFranchiseAndPincode(@Argument String id, @Argument String pincode) {
return this.storeManagementQueryService.getStoresByFranchiseAndPincode(id, pincode);
}
}QueryMapping in the above code example maps the query with the query name defined in the schema file (schema.graphqls)
Store Service
@Service
@Slf4j
public class StoreManagementQueryService {
private final StoreRepository storeRepository;
public StoreManagementQueryService(StoreRepository storeRepository) {
this.storeRepository = storeRepository;
}
public List<Store> getStoresByFranchise(String id) {
try {
return storeRepository.findAllByFranchiseId(id);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public List<Store> getStoresByFranchiseAndPincode(String id, String pincode) {
try {
return storeRepository.findAllByAttributesFranchiseIdAndPincode(id, pincode);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public List<Store> getStoresByPincode(String pincode) {
try {
return storeRepository.findAllByAttributesPincode(pincode);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}Add Data Layer - MongoDB
Data layer for the API to access data stored in the MongoDB data store.
Domain Object
@Getter
@Setter
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Document(collection = "stores")
public class Store {
@Id
private String id;
private String name;
private String description;
private String franchiseId;
private Date created_at;
private Date updated_at;
}Data Repository
@Repository
public interface StoreRepository extends MongoRepository<Store, String> {
@Query(value = "{'attributes.address.pincode' : ?0}")
List<Store> findAllByAttributesPincode(String pincode);
@Query(value = "{'attributes.address.pincode' : ?1, 'franchiseId' : ?0}")
List<Store> findAllByAttributesFranchiseIdAndPincode(String id, String pincode);
List<Store> findAllByFranchiseId(String franchiseId);
}Application Properties
server.port=8080
spring.application.name=GRAPHQL-API
server.servlet.context-path=/api/v1
# Graphql properties
spring.graphql.graphiql.enabled=true
spring.graphql.graphiql.path=/graphiql
spring.graphql.path=/graphql
spring.graphql.schema.file-extensions=.graphqls
spring.graphql.schema.locations=classpath:graphql/**/
# Mongodb properties
spring.data.mongodb.uri={mongodb-url}
logging.level.org.springframework.data.mongodb=DEBUGTesting GraphQL API
There are different ways to test the GraphQL APIs, see below.
Test Using GraphiQL
GraphiQL is built into SpringBoot-GraphQL, as mentioned in application.properties above. To enable GraphQL APIs for testing using GraphiQL, it needs to be enabled.
spring.graphql.graphiql.enabled=true
spring.graphql.graphiql.path=/graphiqlGraphiql URL: http://localhost:8080/api/v1/graphiql?path=/api/v1/graphql
Test Using Postman
To test GraphQL APIs on Postman, follow the steps below
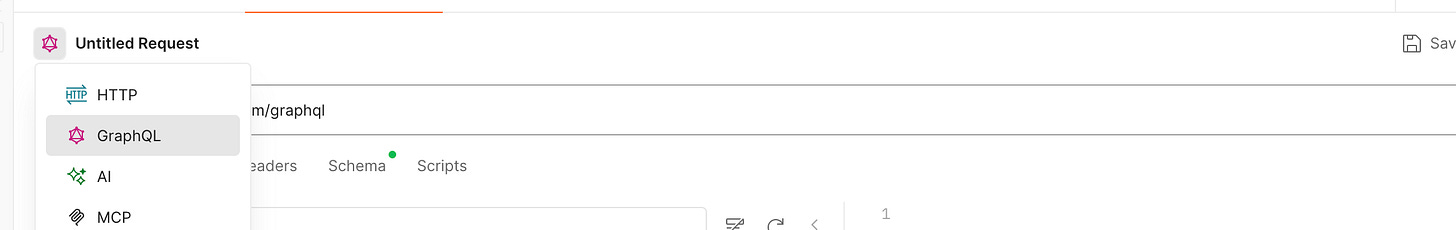
Open a new request tab on Postman. Select GraphQL as shown in the image below
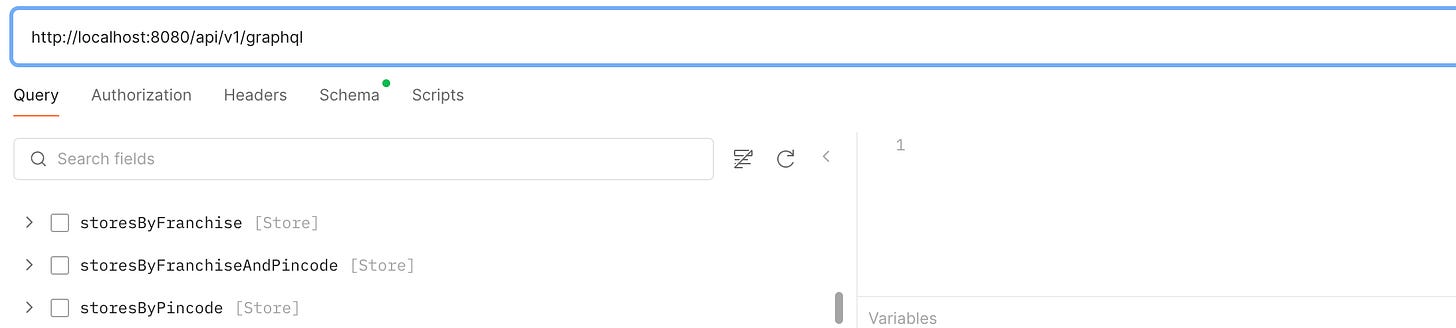
Paste the Server URL. Under the schema tab, select "Using GraphQL introspection." Postman will automatically load the queries in the schema file.
Conclusion
Integrating GraphQL with Spring Boot and MongoDB offers a compelling solution for building modern, efficient, and scalable APIs. This powerful combination empowers developers to overcome the limitations of traditional API designs, delivering flexible data access and a streamlined development workflow. As applications continue to demand more dynamic and precise data interactions, this stack stands out as a robust choice for the future of API development.